what all do i need to start my own super worm supply
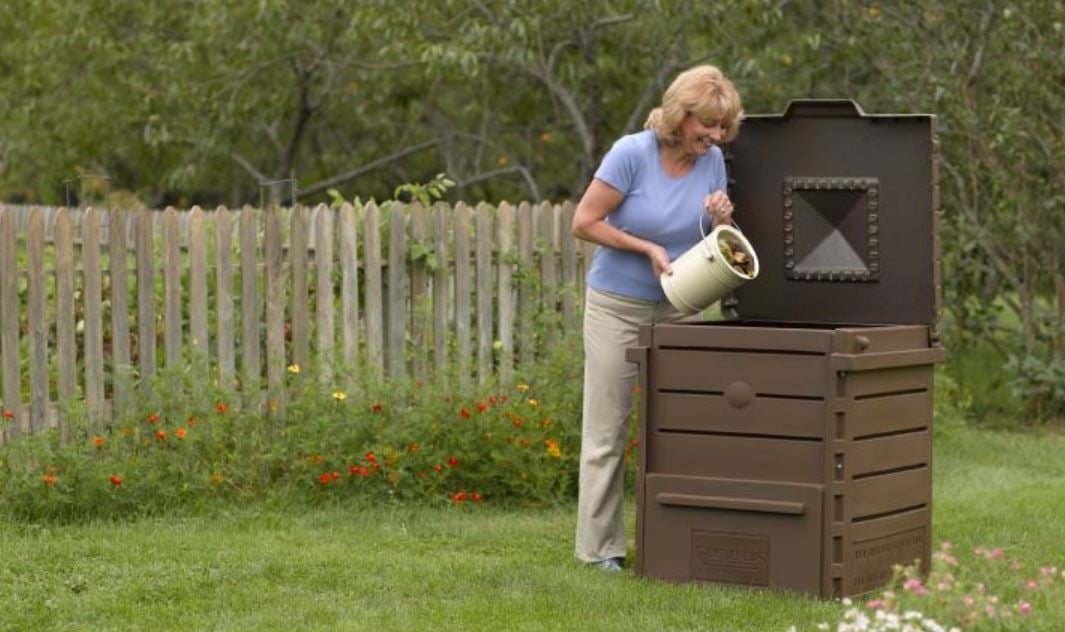

Building and maintaining a compost pile is the surest, easiest manner to become a better gardener. Not only will y'all be producing the best possible food for your garden, but past watching leaves, eggshells, orangish rinds, and grass clippings become transformed into rich compost filled with earthworms and other soil creatures, yous'll be learning what healthy soil is all about.
 Compost is a rich and crumbly blend of partially decomposed organic material that does wonderful things for your garden.
Compost is a rich and crumbly blend of partially decomposed organic material that does wonderful things for your garden.
Compost improves soil structure.
Most gardeners don't start with great soil. Whether yours is hard and compacted, sandy, stony, heavy, or wet, adding compost will ameliorate its texture, h2o-holding capacity, and fertility. Your soil will gradually become fluffy and brown—the ideal dwelling house for healthy plants.
Compost provides a balanced source of establish nutrients.
Even if yous are lucky enough to take cracking soil, y'all can't look that soil to remain rich and productive without replenishing the nutrients that are consumed each growing season. No commercial fertilizer, even i that is totally organic, provides the full spectrum of nutrients that you become with compost. The nutrients are available gradually, equally your plants need them, over a period of months or years. The microorganisms in the compost will too help your plants absorb nutrients from fertilizers more efficiently.
Compost stimulates benign organisms.
Compost is teeming with all kinds of microorganisms and soil animal that help convert soil nutrients into a form that can be readily captivated past your plants. The microorganisms, enzymes, vitamins and natural antibiotics that are present in compost really assist prevent many soil pathogens from harming your plants. Earthworms, millipedes, and other macro-organisms tunnel through your soil, opening upwards passageways for air and water to reach your plants' roots.
Compost is garden insurance.
Even very experienced gardeners oftentimes have soil that is less than perfect. Calculation compost moderates pH and fertility bug, and so you can concentrate on the pleasures of gardening, not the science of your soil'due south chemical limerick. Different organic or inorganic fertilizers, which demand to be applied at the correct time and in the correct amount, compost can be applied at any time and in any corporeality. You lot can't really over-apply it. Plants use exactly what they need, when they demand it.
Tin can a gardener ever have plenty compost? It'south doubtful. Compost is the perfect thing to spread around when y'all are creating a new garden, seeding a new backyard area, or planting a new tree. Compost can be sprinkled effectually plants during the growing flavour or used as a mulch in your perennial gardens. You can add compost to your blossom boxes and deck planters. You tin can likewise use information technology to enrich the potting soil for your indoor plants.
Composts Builds Healthy Soil Across Your Garden and Landscape
Prove all your gardens some love by treating them to regular doses of compost. In spring, compost gets plants off to a strong offset. In fall, fifty-fifty equally air temperatures drop, the soil stays warm and then the compost feeds the all the same-active beneficial organisms.
In the vegetable garden. Amend soil each spring with a layer of compost. You lot tin can gently mix it into the top few inches of soil, or mulch around individual plants or rows. In fall, as you remove spent crops, loosen soil and mix in a 3" to 4" deep layer of compost. Then comprehend bare soil with shredded leaves or straw. The soil will be refreshed for spring planting.
Pamper perennials. As you tidy up perennial gardens — in spring, autumn, or anytime in between — keep a saucepan of compost at hand and then you lot can spread a i" layer around the base of each plant, keeping the compost a few inches from the stems to forestall rot.
Nurture shrubs and trees. Don't take 'em for granted — they're your biggest mural investment! In spring and fall, spread a 3" layer of compost in a wide ring extending well beyond the edge of the canopy. Proceed the compost 6" inches away from stems and trunks to prevent rot.
Requite bulbs a boost. Mix in a few handfuls of compost into each bulb planting hole, or prepare an entire bed past mixing in a generous layer of compost earlier planting.
Lawns are plants, too! Utilise a ane/2" layer of compost over your entire lawn each spring and fall. If soil is compacted, rent an aerator kickoff to open up up the soil and then water will wash the compost down to the grass roots.
How Compost Happens
Organic matter is transformed into compost through the piece of work of microorganisms, soil fauna, enzymes and fungi. When making compost, your chore is to provide the all-time possible environment for these beneficial organisms to exercise their work. If you do then, the decomposition process works very speedily—sometimes in as little as ii weeks. If you don't provide the optimum environment, decomposition will even so happen, simply it may take from several months to several years.
The play a trick on to making an abundance of compost in a short time is to residue the following iv things:
- Carbon. Carbon-rich materials are the free energy food for microorganisms. You tin can identify loftier-carbon plant materials because they are dry, tough, or fibrous, and tan or brown in color. Examples are dry leaves, harbinger, rotted hay, sawdust, shredded paper, and cornstalks.
- Nitrogen. High-nitrogen materials provide the poly peptide-rich components that microorganisms crave to grow and multiply. Freshly pulled weeds, fresh grass clippings, over-ripe fruits and vegetables, kitchen scraps and other moist green matter are the sorts of nitrogen-rich materials you'll probably take on hand. Other high-protein organic matter includes kelp repast, seaweed, manure and animal by-products like blood or bone meal.
- Water. Moisture is very of import for the composting process. Only as well much moisture will drown the microorganisms, and besides little will dehydrate them. A full general rule of pollex is to keep the fabric in your compost pile as moist as a well-wrung sponge. If y'all need to add together water (unchlorinated is best), insert your garden hose into the middle of the pile in several places, or sprinkle the pile with water side by side time you turn it. Using an enclosed container or covering your pile with a tarp will go far easier to maintain the right moisture level.
- Oxygen. To exercise their piece of work near efficiently, microorganisms require a lot of oxygen. When your pile is get-go assembled, in that location volition probably exist plenty of air between the layers of materials. But equally the microorganisms brainstorm to work, they will offset consuming oxygen. Unless you turn or in some fashion aerate your compost pile, they volition run out of oxygen and become sluggish.
Common Compost Ingredients
Brown
High-carbon materials
- corncobs and stalks
- paper
- pine needles
- sawdust or wood shavings
- straw
- vegetable stalks
- dry leaves
Green
High-nitrogen materials
- coffee grounds
- eggshells
- fruit wastes
- grass clippings
- feathers or hair
- fresh leaves
- seaweed
- kitchen scraps
- fresh weeds
- rotted manure
- alfalfa repast
Do I Need a Recipe?
Microorganisms and other soil fauna piece of work most efficiently when the ratio of carbon-rich to nitrogen-rich materials in your compost pile is approximately 25:one (brownish to green) but most people find three parts brown and ane function green works quite well. In practical terms, if yous desire to have an active compost pile, you should include lots of loftier-carbon "brown" materials (such as straw, forest chips, or dry leaves) and a bottom amount of loftier-nitrogen "green" materials (such as grass clippings, freshly pulled weeds, or kitchen scraps).
If yous have an excess of carbon-rich materials and not enough nitrogen-rich materials, your pile may take years to decompose (there is not plenty protein for those microbes!). If your pile has likewise much nitrogen and non enough carbon, your pile volition also decompose very slowly (not enough for the microbes to consume!), and information technology will probably be soggy and smelly along the fashion.
But don't worry about determining the exact carbon content of a material or achieving a precise 25:1 ratio. Composting doesn't need to exist a competitive, goal-oriented job. All organic matter breaks down eventually, no matter what y'all do. If you only use near 3 times as much "brown" materials as "green" materials, you'll exist off to a great start. Accept a look at the sample recipes and check the nautical chart of common compost materials. With experience, you'll become a sense for what works all-time.
Sample Compost Recipes
Recipe 1
- ane part fresh grass clippings
- 1 role dry out leaves
- 1 part good garden soil
Spread the ingredients in 3-inch-deep layers to a meridian of 3 to 4 anxiety.
Recipe 2
- 2 parts fresh grass clippings
- 2 parts straw or spoiled hay
- 1 role good garden soil
Spread ingredients in four-inch layers, adding water if needed.
Recipe 3
- 2 parts dry out leaves
- 1 part fresh grass clippings
- 1 office food scraps
Spread ingredients in 4-inch layers, adding water if needed.
Ingredients to Spice Upwards Your Compost Pile
The following materials tin be sprinkled onto your compost pile as you build each layer. They will add important nutrients and will help speed up the composting process:
- Super Hot Compost Starter, applied at the rate on the packet.
- Garden soil or finished compost (high in microorganisms), 1/2 shovelful on each layer
- Bone repast, blood meal, or alfalfa repast (high in nitrogen), ane/two shovelful on each layer
- Fish waste or manure (loftier in nitrogen), a shovelful on each layer
- Wood stove or fireplace ashes (high in potash and carbon), a shovelful on each layer
- Crushed rock dust (rich in minerals/feeds microbes), a shovelful on each layer
Compost Gets Hot
Oestrus is a past-production of intense microbial activeness. Information technology indicates that the microorganisms are munching on organic matter and converting it into finished compost. The temperature of your compost pile does not in itself affect the speed or efficiency of the decomposition process. But temperature does determine what types of microbes are agile.
There are primarily three types of microbes that work to assimilate the materials in a compost pile. They each work best in a detail temperature range:
The psychrophiles piece of work in cool temperatures—even equally low equally 28 degrees F. Every bit they begin to assimilate some of the carbon-rich materials, they requite off oestrus, which causes the temperature in the pile to rise. When the pile warms to threescore to lxx degrees F, mesophilic bacteria have over. They are responsible for the majority of the decomposition work. If the mesophiles have enough carbon, nitrogen, air, and h2o, they work so difficult that they raise the temperature in the pile to about 100 degrees F. At this indicate, thermophilic bacteria boot in. It is these leaner that can raise the temperature loftier enough to sterilize the compost and kill disease-causing organisms and weed seeds. 3 to 5 days of 155 degrees F. is enough for the thermophiles to exercise their best work.
Getting your compost pile "hot" (140 to 160 degrees F.) is non critical, but information technology does hateful that your compost will be finished and usable inside a month or so. These loftier temperatures also impale most weed seeds, likewise as harmful pathogens that can cause disease problems. Most people don't bother charting the temperature curve in their compost pile. They merely try to get a proficient ratio of carbon to nitrogen, keep the pile moist and well aerated, and wait until everything looks pretty well broken downward.
Commercial activators can aid raise the temperature in your compost pile past providing a concentrated dose of microorganisms and poly peptide. Other effective activators that tin can help to get your pile cooking include humus-rich soil, rotted manure, finished compost, stale blood, and alfalfa meal.
To Turn or Non to Plough
Unless speed is a priority, frequent turning is not necessary. Many people never plow their compost piles. The purpose of turning is to increment oxygen flow for the microorganisms, and to blend undecomposed materials into the middle of the pile. If you lot are managing a hot pile, you'll probably want to plough your compost every 3 to 5 days, or when the interior temperature dips below about 110 degrees F. Monitor the temperature with a compost thermometer; utilize garden shovel, fork or a compost aerator to help plough the pile.
After turning, the pile should heat upward again, equally long every bit there is still undecomposed material to be cleaved down. When the temperature stays pretty constant no thing how much you plough the pile, your compost is probably ready. Though turning can speed the composting process, information technology also releases heat into the air, so you should plow your pile less frequently in common cold weather.
There are several means to assist continue your pile well-aerated, without the hassle of turning:
- Build your pile on a raised wood platform or on a pile of branches.
- Make sure there are air vents in the sides of your compost bin.
- Put ane or two perforated iv" plastic pipes in the center of your pile.
Types of Compost Bins
- Plastic Stationary Bins. These bins are for continuous rather than batch composting. Most units feature air vents along the sides and are made from recycled plastics, such as our Pyramid Composter. Look for a hat that fits securely, and doors to access finished compost. Size should be approximately 3 feet foursquare.
- Tumbling or Rotating Bins. These composters, such every bit our Dual-Batch Compost Tumbler, are for making batches of compost all at once. You accumulate organic materials until y'all take enough to make full the bin, then load it up and rotate it every day or two. If materials are shredded before going into the bin, and yous have plenty of nitrogen, you tin take finished compost in five weeks or less.
- Worm Composting Employing worms to brand compost is chosen vermiculture. Manure worms, crimson worms, and branding worms (the small ones usually sold by commercial breeders) are dynamos when it comes to decomposing organic thing—particularly kitchen scraps. The problem is that these worms cannot tolerate loftier temperatures. Add a scattering of them to an agile compost pile and they'll be dead in an hour. Field worms and night crawlers (common garden worms with one big ring) are killed at even lower temperatures. To maintain a dissever worm bin for composting food scraps, you need a watertight container that tin be kept somewhere that the temperature will remain between l and 80 degrees F. all year-round. Ready-fabricated worm bins are available, but you tin also make your ain. "Red wiggler" compoting worms are bachelor past mail.
| Wire Bin. Use an 11-pes length of 2-inch 10 iv-inch x 36-inch welded, medium-judge fence wire from your local hardware or building supply store. Necktie the ends together to form your hoop. A bin this size holds just over one cubic g of material. Snow fencing can be used in a similar mode. Another option is our 3-Bin Wire Composter, which holds 48 cubic anxiety. | |
| Trash Can Bin. To convert a plastic trash tin into a composter, cut off the bottom with a saw. Drill almost 24 quarter-inch holes in the sides of the can for expert aeration. Bury the lesser of the tin can from several inches to a foot or more below the soil surface and press the loosened soil around the sides to secure it. Partially burying the composter will arrive easier for microorganisms to enter the pile. | 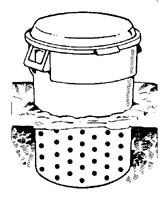 |
| Block or Brick or Stone Bin. Lay the blocks, with or without mortar, leaving spaces between each block to allow aeration. Class three sides of a 3-to four-foot foursquare, roughly 3 to iv feet loftier. |  |
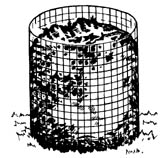
| Woods Pallet Bin. Discarded wooden pallets from factories or stores tin be stood upright to form a bin. Attach the corners with rope, wire, or chain. A quaternary pallet can be used as a floor to increase air menstruation. A used carpet or tarp tin can be placed over the meridian of the pile to reduce moisture loss or continue out rain or snow. | 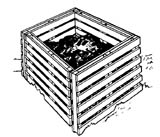 |
| Two- or Three-Bay Wood Bin. Having several bins allows you lot to use ane section for storing materials, one for active composting, and 1 for curing or storing finished compost. Each bin should be approximately 3 10 3 ten 3 feet. Be sure to let air spaces between the sidewall slats, and brand the front walls removable (lift out slats) for easy admission. Lift-up lids are nice. |  |
Source: https://www.gardeners.com/how-to/all-about-composting/5061.html
0 Response to "what all do i need to start my own super worm supply"
Enregistrer un commentaire